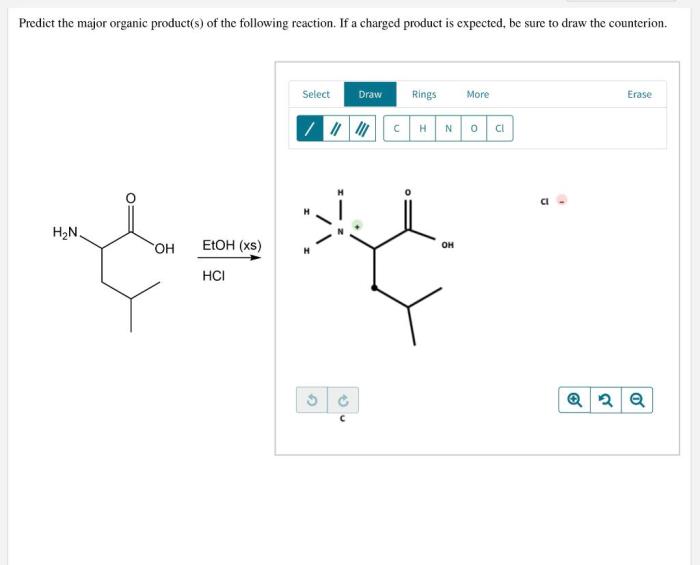
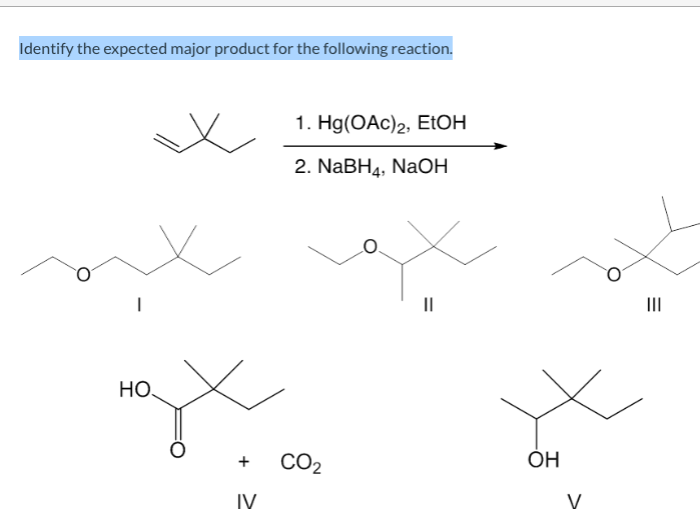
What is the expected product of the following reaction? This question lies at the heart of chemical synthesis, guiding researchers in their quest to design and execute successful reactions. Understanding the factors that determine the expected product is crucial for predicting reaction outcomes and optimizing synthetic strategies.
This comprehensive guide delves into the concept of expected products, exploring the intricacies of reaction analysis, examining specific examples and case studies, and discussing the practical applications and implications of understanding expected products in chemistry.
Expected Product in Chemical Reactions
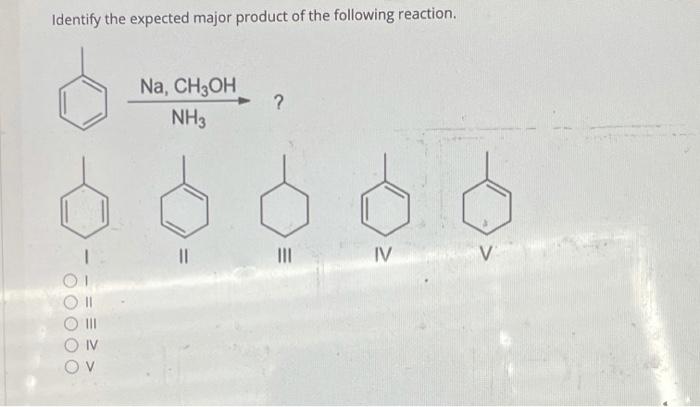
In chemical reactions, the expected product refers to the most likely outcome based on the reactants, reaction conditions, and fundamental chemical principles. Predicting the expected product is crucial for understanding and controlling chemical processes.
Several factors influence the expected product, including:
- Reactant reactivity
- Reaction conditions (temperature, pressure, solvent)
- Reaction mechanism
- Kinetic and thermodynamic factors
Reaction Analysis
Consider the following reaction:
CH 3CH 2Br + NaOH →
- Reactants: CH 3CH 2Br (ethyl bromide), NaOH (sodium hydroxide)
- Products: CH 3CH 2OH (ethanol), NaBr (sodium bromide)
- Reaction conditions: Aqueous solution, room temperature
The reaction proceeds via an S N2 mechanism, where the hydroxide ion (OH –) attacks the electrophilic carbon in ethyl bromide, leading to the formation of ethanol and sodium bromide as the expected products.
Examples and Case Studies
- Combustion of methane:CH 4+ 2O 2→ CO 2+ 2H 2O
- Acid-base neutralization:NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H 2O
- Electrophilic aromatic substitution:C 6H 6+ HNO 3+ H 2SO 4→ C 6H 5NO 2+ H 2O
In some cases, the expected product may differ from the observed product due to factors such as:
- Side reactions
- Unfavorable reaction conditions
- Kinetic or thermodynamic limitations
Applications and Implications, What is the expected product of the following reaction
Understanding expected products is essential in:
- Predicting the outcome of chemical reactions
- Designing synthetic strategies
- Optimizing reaction conditions
- Troubleshooting unexpected results
Unexpected products can provide valuable insights into reaction mechanisms and limitations, leading to improved understanding and control of chemical processes.
Additional Considerations
Other factors that can affect the expected product include:
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Catalysts
- Solvent effects
Computational tools and theoretical models can be employed to predict expected products based on reaction conditions and molecular structures.
Helpful Answers: What Is The Expected Product Of The Following Reaction
What factors influence the expected product of a reaction?
Factors that influence the expected product include the nature of the reactants, reaction conditions (temperature, pressure, solvent), and the presence of catalysts or inhibitors.
How can I predict the expected product of a reaction?
Predicting expected products involves analyzing the reaction mechanism, considering the reactivity and selectivity of the reactants, and utilizing computational tools or theoretical models.
What are the implications of unexpected products in reactions?
Unexpected products can arise due to side reactions or competing pathways. Understanding the reasons for unexpected products is crucial for troubleshooting reactions and developing strategies to minimize their formation.