Amoeba sister video recap dna vs rna and protein synthesis – In this captivating video recap from Amoeba Sister, we delve into the fascinating world of molecular biology, exploring the intricate relationship between DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis. Prepare to unravel the secrets of these fundamental biological processes that govern life’s most essential functions.
Through engaging explanations and vivid illustrations, we’ll uncover the structural and functional differences between DNA and RNA, tracing their roles in protein synthesis. Join Amoeba Sister on this educational journey as we unravel the mysteries of these molecular building blocks.
Amoeba Sister Video Recap
The Amoeba Sisters video provides a comprehensive overview of the structure and function of amoebas, as well as the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Amoebas are single-celled organisms that move by extending and contracting their cytoplasm. They have a simple structure, consisting of a nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell membrane. Amoebas are found in a wide variety of habitats, including soil, water, and the human body.
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
The following table summarizes the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells:
| Characteristic | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | No nucleus | True nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane |
| Organelles | No membrane-bound organelles | Membrane-bound organelles, including mitochondria, chloroplasts, and Golgi apparatus |
| DNA | Circular DNA located in the cytoplasm | Linear DNA located in the nucleus |
| Ribosomes | 70S ribosomes | 80S ribosomes |
| Cell Division | Binary fission | Mitosis or meiosis |
DNA vs. RNA: Amoeba Sister Video Recap Dna Vs Rna And Protein Synthesis
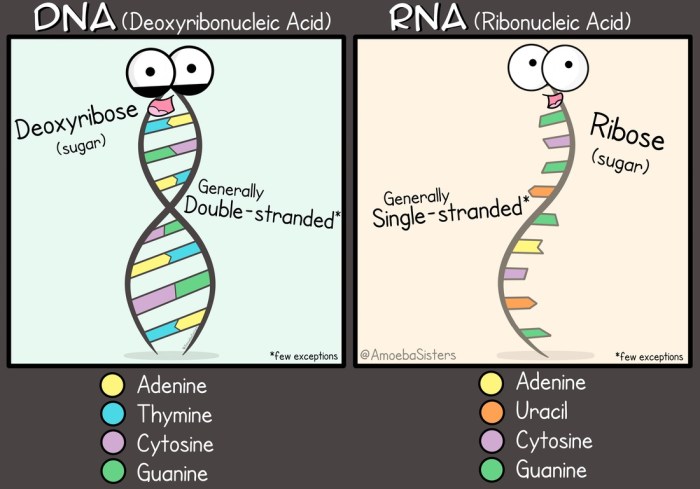
DNA and RNA are two types of nucleic acids that play essential roles in the cell. DNA stores the genetic information of the cell, while RNA helps to translate that information into proteins.
DNA is a double-stranded molecule that consists of four different nucleotides: adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. The sequence of these nucleotides determines the genetic code of the cell.
RNA is a single-stranded molecule that consists of four different nucleotides: adenine, uracil, guanine, and cytosine. RNA is synthesized from DNA by a process called transcription. There are three main types of RNA: messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA).
mRNA carries the genetic code from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where it is translated into proteins by ribosomes. tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes, where they are added to the growing polypeptide chain.
rRNA is a component of ribosomes, the structures that assemble proteins.
Key Differences between DNA and RNA, Amoeba sister video recap dna vs rna and protein synthesis
- DNA is double-stranded, while RNA is single-stranded.
- DNA contains the nucleotides adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine, while RNA contains the nucleotides adenine, uracil, guanine, and cytosine.
- DNA is found in the nucleus, while RNA is found in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
- DNA is used to store genetic information, while RNA is used to translate genetic information into proteins.
Protein Synthesis

Protein synthesis is the process by which cells create proteins. Proteins are essential for a wide variety of cellular functions, including metabolism, growth, and repair.
Protein synthesis occurs in two steps: transcription and translation.
Transcription
Transcription is the process by which DNA is copied into RNA. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and is carried out by an enzyme called RNA polymerase.
RNA polymerase binds to a specific region of DNA called the promoter. RNA polymerase then unwinds the DNA and synthesizes a complementary strand of RNA. The RNA strand is then released from the DNA and travels to the cytoplasm.
Translation
Translation is the process by which RNA is translated into proteins. Translation occurs in the cytoplasm and is carried out by ribosomes.
Ribosomes bind to the mRNA strand and read the sequence of codons. Each codon consists of three nucleotides and codes for a specific amino acid. The ribosome then binds to a tRNA molecule that carries the corresponding amino acid.
The ribosome moves along the mRNA strand, adding amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain. Once the polypeptide chain is complete, it is released from the ribosome and folded into a specific conformation.
The following flowchart illustrates the process of protein synthesis:
Question Bank
What is the main difference between DNA and RNA?
DNA is a double-stranded molecule, while RNA is a single-stranded molecule. DNA contains the genetic code for an organism, while RNA plays a role in protein synthesis.
What is the role of ribosomes in protein synthesis?
Ribosomes are cellular structures that assemble proteins by reading the genetic code carried by mRNA.
How does protein synthesis contribute to cellular function?
Proteins are essential for a wide range of cellular functions, including metabolism, growth, and reproduction.