The NRP Epinephrine Dose 8th Edition, a cornerstone in neonatal resuscitation, stands as a testament to the unwavering commitment to improving newborn outcomes. This updated edition brings forth significant advancements, shaping the landscape of neonatal care and empowering healthcare providers with the knowledge and tools necessary to effectively manage life-threatening emergencies.
Within the realm of this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of the NRP Epinephrine Dose 8th Edition, exploring its purpose, significance, indications, dosage, administration, precautions, monitoring, and follow-up care. Through this exploration, we aim to equip healthcare providers with a profound understanding of this critical intervention, enabling them to confidently and competently administer epinephrine in newborns, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes.
Overview of NRP Epinephrine Dose 8th Edition

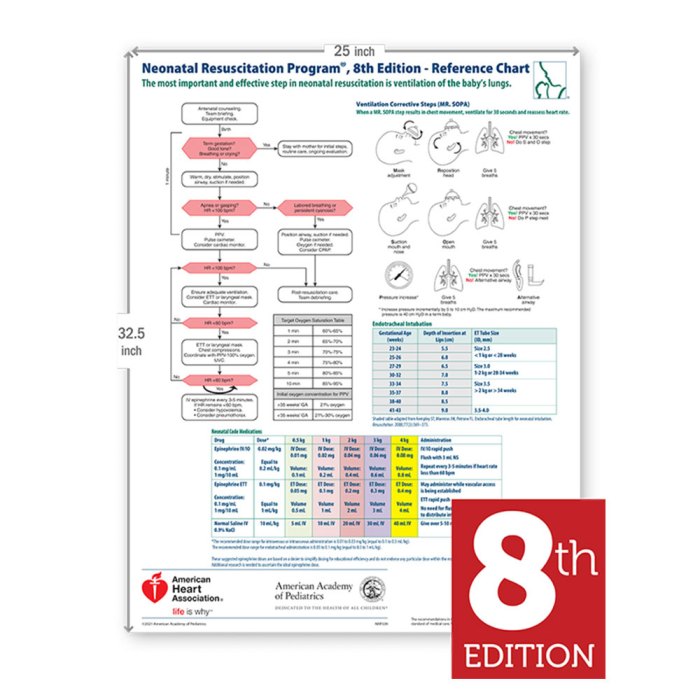
The NRP Epinephrine Dose 8th Edition provides updated guidelines for the administration of epinephrine in newborn resuscitation. This edition incorporates the latest research and evidence-based practices to optimize the safe and effective use of epinephrine in neonates.
The key updates in the 8th edition include:
- Revised dosing recommendations based on weight-based dosing
- New indications for epinephrine administration
- Updated guidelines for monitoring and follow-up care
Indications for Epinephrine Administration
Epinephrine is indicated for administration in newborns who meet the following criteria:
- Absence of spontaneous respirations or gasping after initial resuscitation efforts
- Heart rate less than 60 beats per minute (bpm) after 30 seconds of chest compressions
- Systolic blood pressure less than 60 mmHg after 30 seconds of chest compressions
Epinephrine is also indicated for use in newborns with suspected or confirmed anaphylaxis, supraventricular tachycardia, or ventricular fibrillation.
Dosage and Administration
The recommended dose of epinephrine for newborns is 0.01 mg/kg, given as an intravenous or intraosseous injection. The dose may be repeated every 3-5 minutes as needed.
Epinephrine should be administered via the umbilical vein or intraosseous infusion if intravenous access is not available.
The proper technique for epinephrine administration is as follows:
- Draw up the correct dose of epinephrine into a syringe.
- Inject the epinephrine into the umbilical vein or intraosseous infusion.
- Flush the vein or infusion with 0.9% saline.
Precautions and Contraindications
Epinephrine should be used with caution in newborns with the following conditions:
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Hypertension
- Thyroid disorders
Epinephrine is contraindicated in newborns with the following conditions:
- Ventricular septal defect
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- Severe pulmonary hypertension
Monitoring and Follow-Up: Nrp Epinephrine Dose 8th Edition
After epinephrine administration, it is important to monitor the newborn’s vital signs closely.
The following parameters should be monitored:
- Heart rate
- Respiratory rate
- Blood pressure
- Oxygen saturation
The frequency of monitoring should be based on the newborn’s clinical status.
Follow-up care after epinephrine administration may include:
- Echocardiography to evaluate for cardiac abnormalities
- Electrocardiography to evaluate for arrhythmias
- Blood tests to evaluate for electrolyte imbalances
Top FAQs
What are the indications for epinephrine administration in newborns?
Epinephrine is indicated in newborns experiencing cardiac arrest or profound bradycardia unresponsive to initial resuscitation efforts.
What is the recommended epinephrine dose for newborns?
The recommended epinephrine dose for newborns is 0.01 mg/kg, administered via the endotracheal tube or intraosseous route.
What are the precautions associated with epinephrine administration in newborns?
Precautions include potential arrhythmias, hypertension, and hyperglycemia. Close monitoring is essential during and after epinephrine administration.