A&p flix activity dna replication – A&P Flix Activity: DNA Replication embarks on an enthralling journey into the realm of genetics, unraveling the intricate mechanisms that govern the replication of DNA, the blueprint of life. This captivating exploration delves into the significance, key steps, and regulation of DNA replication, providing a comprehensive understanding of this fundamental biological process.
DNA replication lies at the heart of cell division, ensuring the faithful transmission of genetic information to daughter cells. Through a series of precisely orchestrated steps, DNA unwinds, nucleotides are added, and new strands are synthesized, guaranteeing the preservation of genetic integrity.
A&P Flix Activity: DNA Replication Overview: A&p Flix Activity Dna Replication
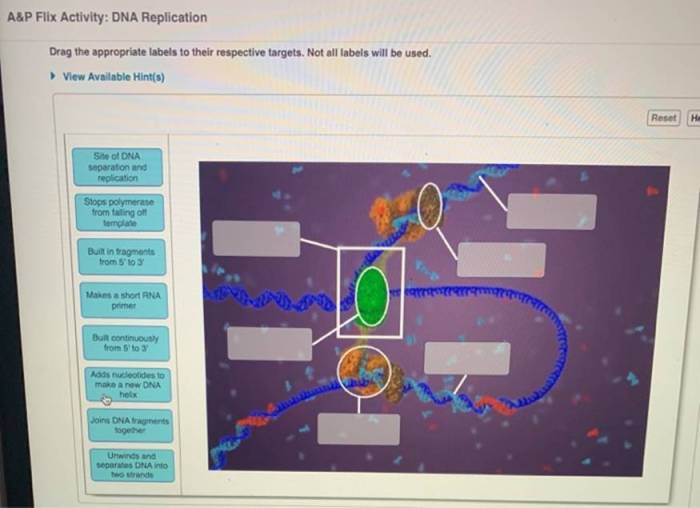
DNA replication is a fundamental process in cell division, ensuring the accurate transmission of genetic information to daughter cells. It involves the unwinding of the DNA double helix, separation of the two strands, and synthesis of two new complementary strands.
This process is facilitated by various enzymes, including helicase, primase, and DNA polymerase. A visual representation of the DNA replication process helps illustrate the key steps and interactions involved.
A&P Flix Activity: DNA Replication Initiation
The origin of replication serves as the starting point for DNA replication. Helicase unwinds the DNA double helix, creating a replication fork. Primase synthesizes short RNA primers, which provide a starting point for DNA polymerase. DNA polymerase III synthesizes new DNA strands in the 5′ to 3′ direction, adding nucleotides that are complementary to the template strand.
Leading and lagging strands are formed due to the antiparallel nature of the DNA double helix.
A&P Flix Activity: DNA Replication Elongation, A&p flix activity dna replication
DNA polymerase III continues to synthesize new DNA strands, adding nucleotides one by one. It possesses proofreading capabilities to ensure the accuracy of the replication process. On the lagging strand, DNA polymerase I synthesizes short fragments known as Okazaki fragments, which are later joined by DNA ligase.
A&P Flix Activity: DNA Replication Termination
Specific signals indicate the completion of DNA replication. Telomerase maintains chromosome integrity by adding repetitive sequences to the ends of chromosomes. Errors in DNA replication can lead to mutations and genetic instability, emphasizing the importance of DNA replication fidelity.
A&P Flix Activity: DNA Replication Regulation
The initiation and progression of DNA replication are tightly regulated by various factors. Cell cycle checkpoints ensure that DNA replication occurs at the appropriate time and with high accuracy. DNA damage can trigger DNA repair mechanisms to maintain genome stability.
Essential FAQs
What is the significance of DNA replication?
DNA replication is essential for cell division, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the genetic material.
What are the key steps involved in DNA replication?
DNA replication involves unwinding the DNA double helix, synthesizing new strands using DNA polymerase, and proofreading to ensure accuracy.
How is DNA replication regulated?
DNA replication is tightly regulated to ensure accurate and timely duplication of the genetic material, involving factors such as cell cycle checkpoints and DNA damage response mechanisms.